
Hernias are a common medical condition that can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. While not always life-threatening, they can cause discomfort, and if left untreated, may lead to serious complications. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what a hernia is, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Is a Hernia?
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot or tear in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This can result in a bulge or lump that may be painful, especially when straining, lifting heavy objects, or even coughing.
The most common areas for hernias to occur are the abdomen, groin, and upper thigh. Although some hernias are painless, they can worsen over time and may require surgical intervention.
Types of Hernia
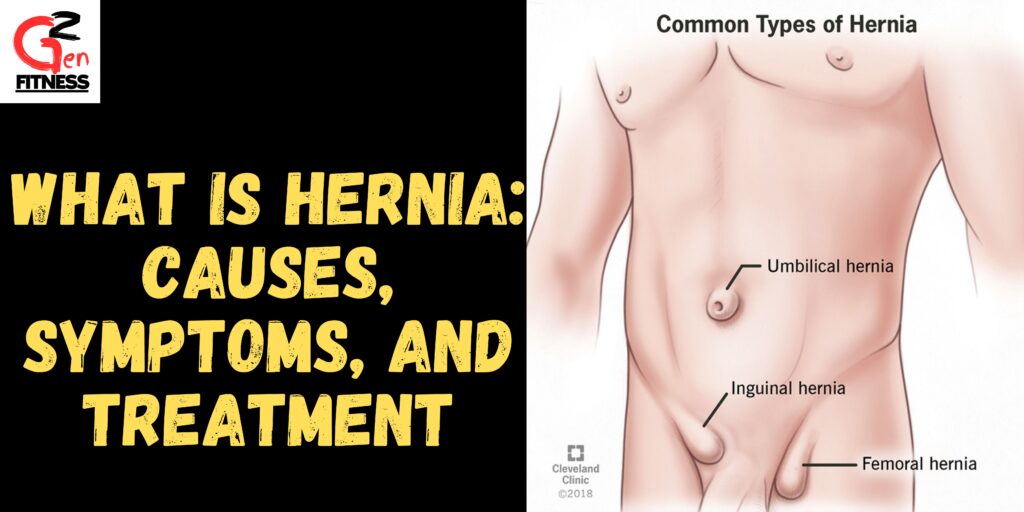
Hernias can occur in different parts of the body, but the most common types include:
- Inguinal Hernia: This is the most common type of hernia, especially in men. It occurs when part of the intestine or fat pushes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall into the inguinal canal, which is located in the groin.
- Femoral Hernia: More common in women, a femoral hernia happens when tissue pushes through the muscle wall into the upper thigh, near the groin.
- Umbilical Hernia: This occurs when part of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall near the navel (belly button). It is common in newborns and infants but can also affect adults.
- Hiatal Hernia: A hiatal hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. This type of hernia is often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Incisional Hernia: This type can occur after surgery when tissue pushes through the incision site or the scar from a previous surgery, leading to a bulge or protrusion.
Causes of Hernia
Several factors can contribute to the development of a hernia. These include:
- Weakness in the Abdominal Muscles: This can be congenital (present from birth) or develop over time due to factors like aging or injury.
- Heavy Lifting: Lifting heavy objects without proper technique can increase intra-abdominal pressure, leading to a hernia.
- Straining: Chronic constipation, coughing, or straining during urination can create excess pressure in the abdomen, contributing to hernia development.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts extra strain on the abdominal muscles.
- Pregnancy: The increased pressure inside the abdomen during pregnancy can lead to hernias, especially umbilical hernias.
- Previous Surgery: An incision or scar from a previous surgery can create a weak spot in the abdominal wall, making it more susceptible to hernias.
Symptoms of Hernia
The symptoms of a hernia can vary depending on the type and severity, but common signs include:
- A noticeable bulge or lump in the affected area, which may increase in size over time.
- Pain or discomfort, especially when bending, lifting, or coughing.
- A heavy or dragging sensation in the groin or abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting in severe cases, particularly if the hernia becomes trapped or strangulated.
- Burning or aching at the site of the bulge.
In some cases, a hernia may not present noticeable symptoms, but it can still be detected during a physical examination.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately:
- Severe pain or swelling at the hernia site.
- A hernia that cannot be pushed back in (incarcerated hernia).
- Nausea, vomiting, or difficulty passing gas or having a bowel movement.
- Fever or signs of infection at the hernia site.
These could be signs of a strangulated hernia, a serious condition that occurs when the blood supply to the trapped tissue is cut off. This requires emergency surgery to prevent life-threatening complications.
Treatment Options for Hernia
Not all hernias require surgery, but treatment depends on the type of hernia, its size, and symptoms. Here are the most common options:
- Watchful Waiting: For small, painless hernias, a doctor may recommend monitoring the condition without immediate intervention.
- Surgery: Surgery is the most effective way to repair a hernia. There are two main types of hernia surgery:
- Open Surgery: The surgeon makes an incision near the hernia site, pushes the protruding tissue back into place, and repairs the weakened muscle wall with stitches or mesh.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions and using a camera to guide the repair. It usually results in a quicker recovery with less scarring.
- Lifestyle Changes: In cases of hiatal hernias, making dietary adjustments to avoid foods that trigger acid reflux and losing weight can help manage symptoms.
Preventing Hernia
While not all hernias can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Avoid heavy lifting without proper technique.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on your abdominal muscles.
- Exercise regularly to strengthen your core muscles.
- Avoid straining during bowel movements by eating a fiber-rich diet to prevent constipation.
- Quit smoking, as chronic coughing can increase the risk of hernia.
Conclusion
A hernia, though common, should not be ignored. If you notice any symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With the right approach, many hernias can be effectively managed or repaired, allowing you to return to your daily activities with minimal disruption.
By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and taking preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing a hernia and avoid potential complications.
Read our latest articles: https://genzfitness.in/
Free stock market course for Genz– https://genzfitness.in/free-stock-market-course-for-genz-4-formulas/
Best Book to read in 2024- https://eatyourproblems.store/





